
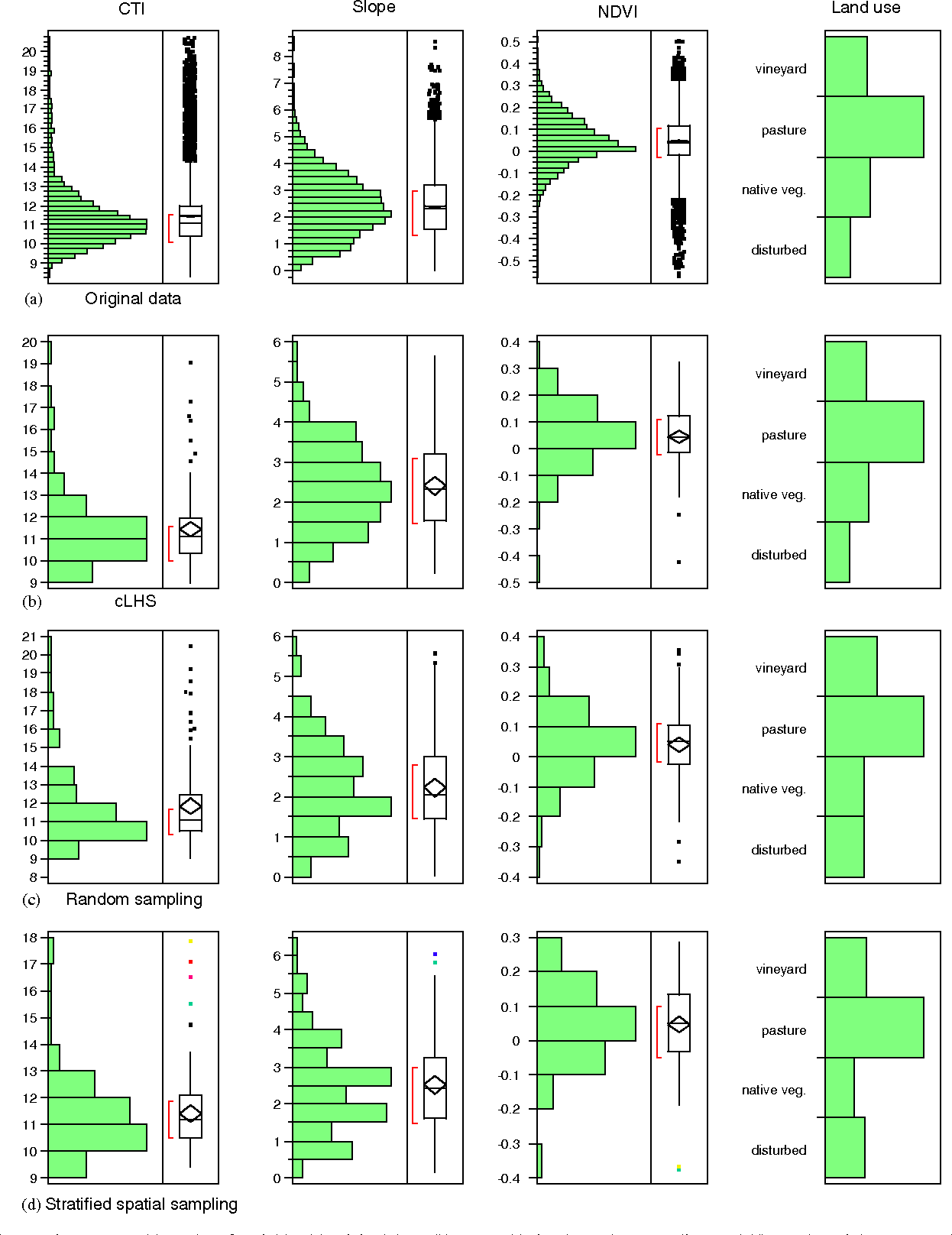
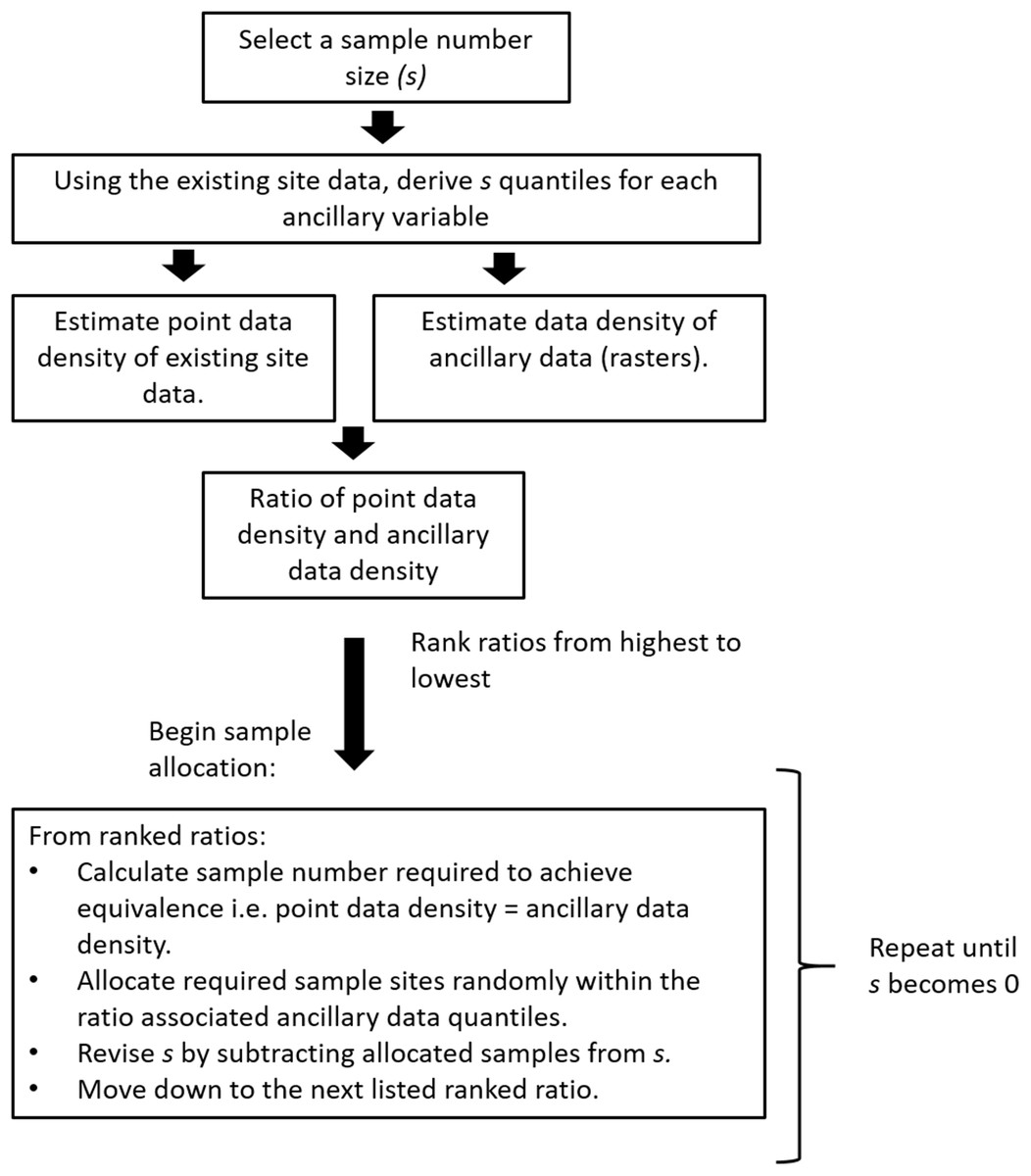
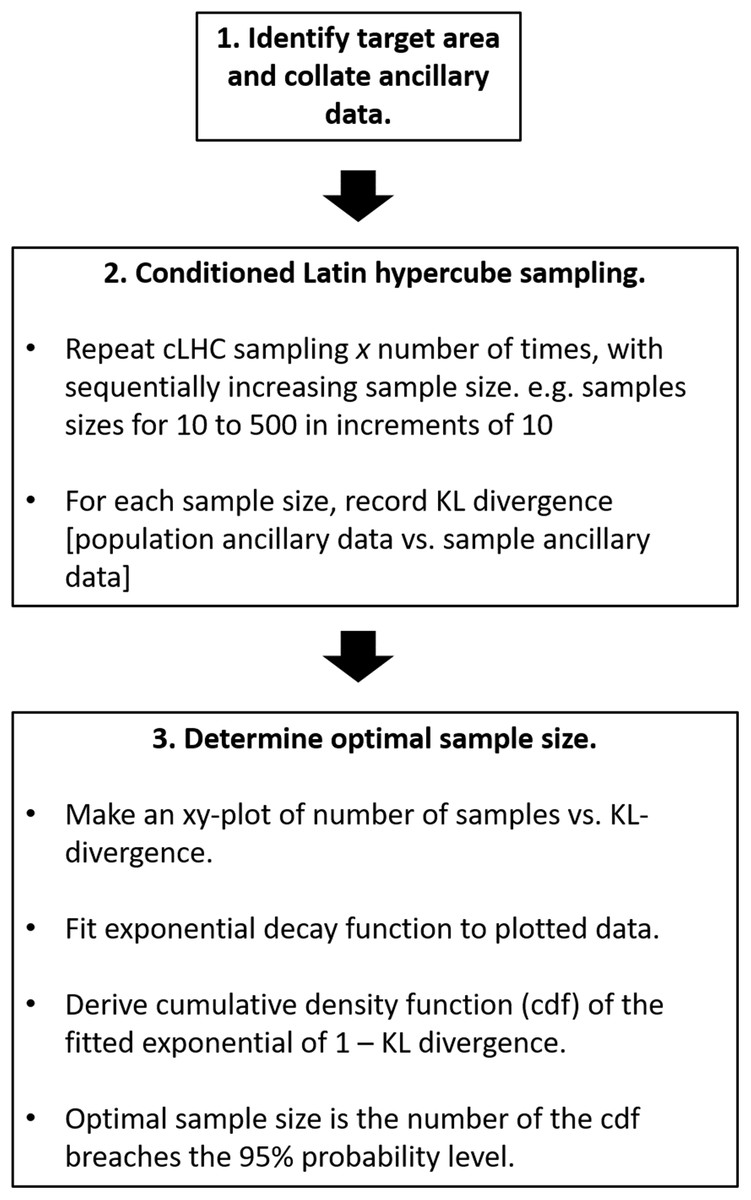
To obtain the Latin Hypercube, let m be the number of random variables and n the. This procedure guar-antees a sparse but homogeneous cover of the sampling space. To build a surrogate model, it is recommended to use an initial sample size equal to 15 times the number of design variables. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures 12 (2015) 624-648 pled only once (McKay et al., 1979 Olsson et al., 2003), such as in Figure 1. Radial basis neural networks showed the best overall performance in global exploration characteristics as well as tendency to find the approximate optimal solution for the majority of tested problems. The surrogate models were analyzed in terms of global exploration (accuracy over the domain space) and local exploitation (ease of finding the global optimum point). sampling approach without the need for a reconnaissance survey to. The important findings are illustrated using Box-plots. Spatial conditioned Latin hypercube sampling (scLHS) is a novel approach based on the.
The three surrogate models, namely, response surface approximation, Kriging, and radial basis neural networks were tested.
The analysis was carried out for two types of problems: (1) thermal-fluid design problems (optimizations of convergent-divergent micromixer coupled with pulsatile flow and boot-shaped ribs), and (2) analytical test functions (six-hump camel back, Branin-Hoo, Hartman 3, and Hartman 6 functions). To overcome these challenges, the PSS method is coupled with a new method called Latinized stratified sampling (LSS) that produces sample sets that are. The present study aimed at evaluating the performance characteristics of various surrogate models depending on the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) procedure (sample size and spatial distribution) for a diverse set of optimization problems. Ficklin, Yuzhou Luo and Minghua Zhang Department of Land, Air and Water Resources, University of California, Davis, CA 95616, USA Abstract: Bracketing the uncertainty of streamow and agricultural runoff under climate change is critical for proper future water resource management in agricultural. The exploration/exploitation properties of surrogate models depend on the size and distribution of design points in the chosen design space. Latin hypercube sampling is widely used design-of-experiment technique to select design points for simulation which are then used to construct a surrogate model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
